
Managing alertness, travel comfort, and relaxation for optimal well-being
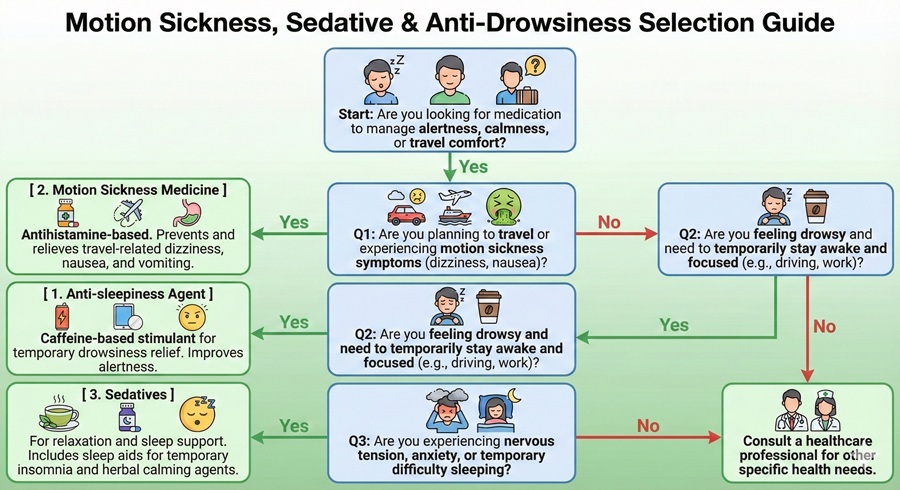
This category encompasses medications that help manage the body's alertness, comfort during travel, and ability to relax and sleep. These three distinct product types address opposite but equally important needs: staying awake when necessary, preventing travel discomfort, and achieving calm and rest when needed.
Each subcategory serves a specific purpose and should be chosen based on your immediate needs. Understanding the differences between these medications is essential for safe and effective use.
| Category | Primary Effect | When to Use | Main Ingredients | Key Caution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-sleepiness Agent | Increases alertness and reduces drowsiness | During driving, work, or when staying awake is necessary | Caffeine, stimulants | Not a substitute for sleep; may cause jitteriness |
| Motion Sickness Medicine | Prevents dizziness, nausea, and vomiting during travel | 30-60 minutes before travel; can also relieve existing symptoms | Antihistamines (dimenhydrinate, meclizine) | May cause drowsiness; avoid driving after use |
| Sedatives | Reduces tension and promotes relaxation or sleep | Before bedtime for sleep; during day for calming (herbal types) | Antihistamines, herbal extracts (Kampo) | Do not drive or operate machinery; avoid alcohol |
Contains caffeine that blocks adenosine receptors in the brain, reducing the sensation of tiredness and temporarily increasing alertness. Effects typically begin within 15-30 minutes.
These products are for temporary use only and should never replace proper sleep. Do not exceed recommended dosage. Not suitable for children, pregnant women, or those with caffeine sensitivity. Avoid using close to bedtime as it may interfere with sleep.
Antihistamines suppress the vestibular system signals that cause motion sickness. They reduce conflicting messages between the eyes and inner ear, preventing dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
Most effective when taken 30-60 minutes before travel. Can provide relief even after symptoms begin. Protection lasts several hours, suitable for extended journeys. May cause drowsiness, so avoid driving after taking.
Traditional Japanese formulations like Yokukansan use multiple medicinal plants working synergistically to calm the nervous system. Preferred by those seeking natural alternatives with potentially fewer side effects.
For temporary use only (typically 5-7 days). Do not combine with alcohol. Sleep-inducing types should not be taken before driving or operating machinery. If symptoms persist beyond 2 weeks, consult a healthcare provider.
DO NOT take anti-sleepiness agents and sedatives on the same day. These products have opposite effects and combining them can be dangerous.
If you need multiple types of medication, consult a pharmacist or doctor for safe timing and combinations.
Prioritize 7-9 hours of sleep nightly. Take short breaks during long drives. Stay hydrated. Maintain regular sleep schedule.
Sit in front seats. Focus on horizon. Avoid reading in vehicles. Get fresh air. Avoid heavy meals before travel.
Maintain consistent sleep schedule. Create dark, cool sleeping environment. Limit screen time before bed. Practice relaxation techniques.
Exercise regularly. Practice mindfulness or meditation. Maintain social connections. Seek counseling if needed.
Browse our complete selection of alertness, travel, and relaxation medications
View All Products